What Makes Prefab Houses the Future of Modern Living?
2025-09-18
The global housing industry is undergoing a major transformation as people search for faster, more affordable, and sustainable ways to build homes. Among the most notable innovations in recent decades is the prefabricated house, often called a prefab house.
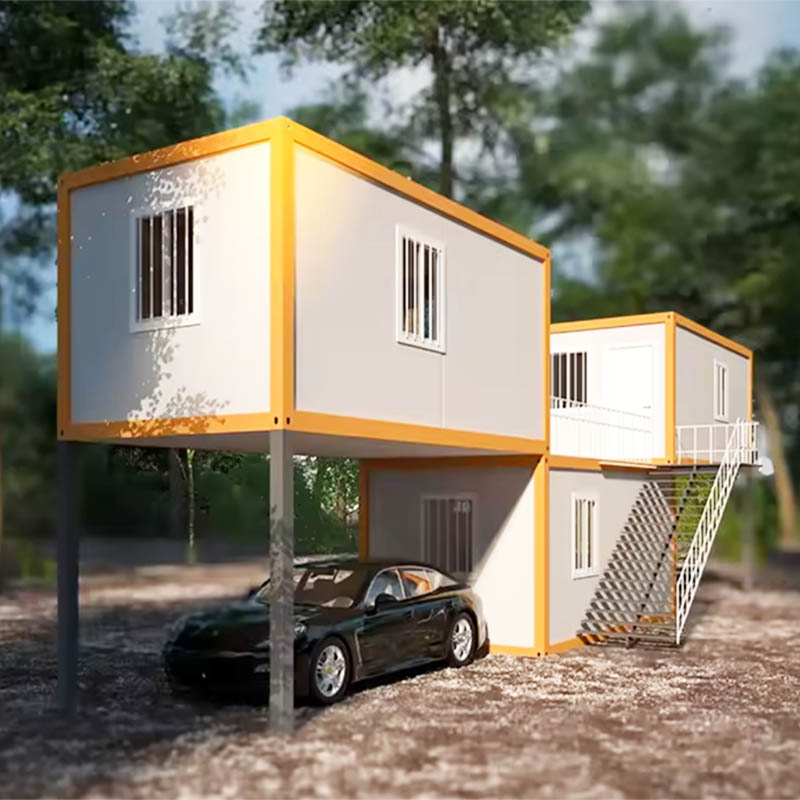
A prefab house is a dwelling that is manufactured off-site in sections, modules, or panels, then transported and assembled at the final location. Unlike traditional brick-and-mortar construction, which is labor-intensive and time-consuming, prefab houses streamline the entire building process. Prefab homes can range from compact modular units for urban housing projects to large multi-story residences and even commercial spaces.
The growing demand for prefab houses stems from several factors:
-
Speed of construction: A prefab home can be ready in a fraction of the time compared to conventional methods.
-
Cost efficiency: Factory-controlled production reduces waste, labor costs, and delays.
-
Sustainability: Many prefab designs incorporate energy-efficient materials, renewable energy systems, and sustainable supply chains.
-
Flexibility: Prefab houses can be customized for size, layout, design, and functionality.
-
Quality control: Manufacturing in controlled environments ensures consistent standards and minimizes construction defects.
As urban populations grow and affordable housing shortages continue, prefab homes are no longer seen as temporary solutions but as a viable mainstream choice. Countries across North America, Europe, and Asia are adopting prefab technologies to meet the rising demand for sustainable and scalable housing.
What Are the Key Features and Specifications of Prefab Houses?
Prefab houses are not one-size-fits-all. They come in various styles and specifications to meet different lifestyle needs and environmental conditions. Understanding the technical parameters is essential for buyers, developers, and investors.
Common Types of Prefab Houses
-
Modular Homes – Built in sections or modules, then transported and assembled on-site.
-
Panelized Homes – Walls, floors, and roof panels are prefabricated and then assembled on location.
-
Pre-Cut Homes – Components like beams and frames are cut in factories and shipped for on-site assembly.
-
Container Homes – Built using repurposed shipping containers, popular for eco-friendly and modern living.
Technical Parameters of Prefab Houses
| Parameter | Specification Options |
|---|---|
| Structure Material | Light steel frame, reinforced concrete, wood, hybrid systems |
| Wall Panels | EPS cement board, PU sandwich panel, fiber cement, gypsum board |
| Roofing | Steel sheets, asphalt shingles, eco-roof tiles, insulated panels |
| Flooring | Plywood, laminate, tiles, vinyl, engineered wood |
| Insulation | Rock wool, polyurethane foam, glass wool, EPS |
| Design Life | 50–100 years depending on material and maintenance |
| Assembly Time | 1–4 weeks depending on size and complexity |
| Energy Options | Solar integration, smart HVAC, rainwater harvesting |
Advantages of Prefab Specifications
-
Durability: High-strength frames and insulation make prefab houses reliable in diverse climates.
-
Energy Efficiency: Advanced insulation reduces heating and cooling costs.
-
Customization: Buyers can choose layouts, materials, and finishes according to preference.
-
Mobility: In some designs, prefab houses can be relocated if necessary.
By offering flexible configurations and technical innovations, prefab houses meet modern demands for sustainability, efficiency, and adaptability.
What Should You Consider Before Choosing a Prefab House?
For homeowners and investors, choosing a prefab house is not only about design but also about practical decision-making. Before committing, it’s important to evaluate several aspects that affect long-term value, comfort, and compliance with regulations.
Key Considerations When Selecting a Prefab House
-
Location and Land Requirements
-
Verify zoning laws, soil conditions, and land size before choosing a prefab model.
-
Ensure local regulations allow modular or prefab construction.
-
-
Budget Planning
-
Prefab houses are generally cheaper than traditional homes, but costs vary by material, design, and finishes.
-
Consider land, transportation, installation, and utility connection costs.
-
-
Design and Layout
-
Prefab homes allow customization in floor plans and aesthetics.
-
Choose between open-concept layouts, multi-level structures, or compact eco-friendly units.
-
-
Climate Compatibility
-
Materials and insulation should match the local climate.
-
Roof design must account for snow load, wind resistance, or high temperatures.
-
-
Sustainability Features
-
Incorporate solar panels, water-saving systems, or smart appliances to maximize eco-friendliness.
-
-
Supplier Reliability
-
Work with trusted suppliers who can provide warranties, after-sales support, and compliance with safety standards.
-
Benefits of Choosing Wisely
-
Faster project completion with minimal delays.
-
Higher resale value due to modern designs and energy efficiency.
-
Long-term cost savings from durable construction.
-
Peace of mind knowing your home complies with legal and safety requirements.
Common FAQs About Prefab Houses
Q1: What is the average lifespan of a prefab house?
A: Prefab houses typically last between 50 to 100 years, depending on the quality of materials and maintenance. Steel and concrete structures tend to have the longest durability, while wood-frame prefab houses may require more frequent upkeep.
Q2: What permits are required to build a prefab house?
A: Permit requirements vary by region, but in most cases, you will need zoning approval, a building permit, and utility connection permits. Some jurisdictions treat prefab houses the same as conventional homes, while others have specific codes for modular or prefabricated structures. Consulting with local authorities or your supplier ensures compliance.
What Does the Future Hold for Prefab Houses?
The future of housing is being redefined by technological innovation, environmental priorities, and shifting consumer preferences. Prefab houses are at the heart of this change, offering smart solutions for urban development, affordable housing, and eco-friendly lifestyles.
Trends Shaping the Prefab Industry
-
Green Construction: Increased demand for low-carbon materials and renewable energy integration.
-
Smart Homes: Integration of IoT devices, automated lighting, and climate control in prefab designs.
-
Urban Solutions: Prefab units for high-density cities where land is scarce.
-
Affordable Housing: Governments adopting prefab projects to reduce homelessness and improve access to housing.
-
Global Expansion: Prefab technologies gaining popularity in emerging economies for quick and reliable construction.
Why Prefab Houses Will Continue to Grow
As populations expand and environmental concerns intensify, prefab houses stand out as a sustainable alternative to traditional construction. They reduce waste, shorten timelines, and offer greater design freedom, making them highly attractive to both individuals and large-scale developers.
At Yilong, we are committed to delivering high-quality prefab houses designed for durability, sustainability, and comfort. With advanced production techniques, customizable designs, and reliable after-sales support, we provide solutions tailored to meet modern housing demands. Whether you’re seeking a single-family residence, a multi-unit project, or a commercial prefab solution, our team ensures that every detail meets international quality standards.
For more information, project inquiries, or personalized consultations, contact us today and discover how Yilong can help you build the future of living with prefab houses.